Describe the Structure and Function of Transfer Rna
It is the base pairing between the tRNA and mRNA that allows for the correct amino acid to be inserted in the polypeptide chain being synthesized Figure 1023. Transfer RNA tRNA is that type of RNA that transfer amino acids to the ribosome for the synthesis of proteins.

Transfer Rna Trna Definition Structure Processing Types Functions
The secondary structure of tRNA is clover leaf-like but the 3-D structure is inverted L-shaped.
. Bases that have a single ring structure thymine and cytosine What are the functions of DNA. RRNA are responsible for reading the order of amino acids and linking amino acids together. Transfer RNA retrieves the materials that the rRNA calls for.
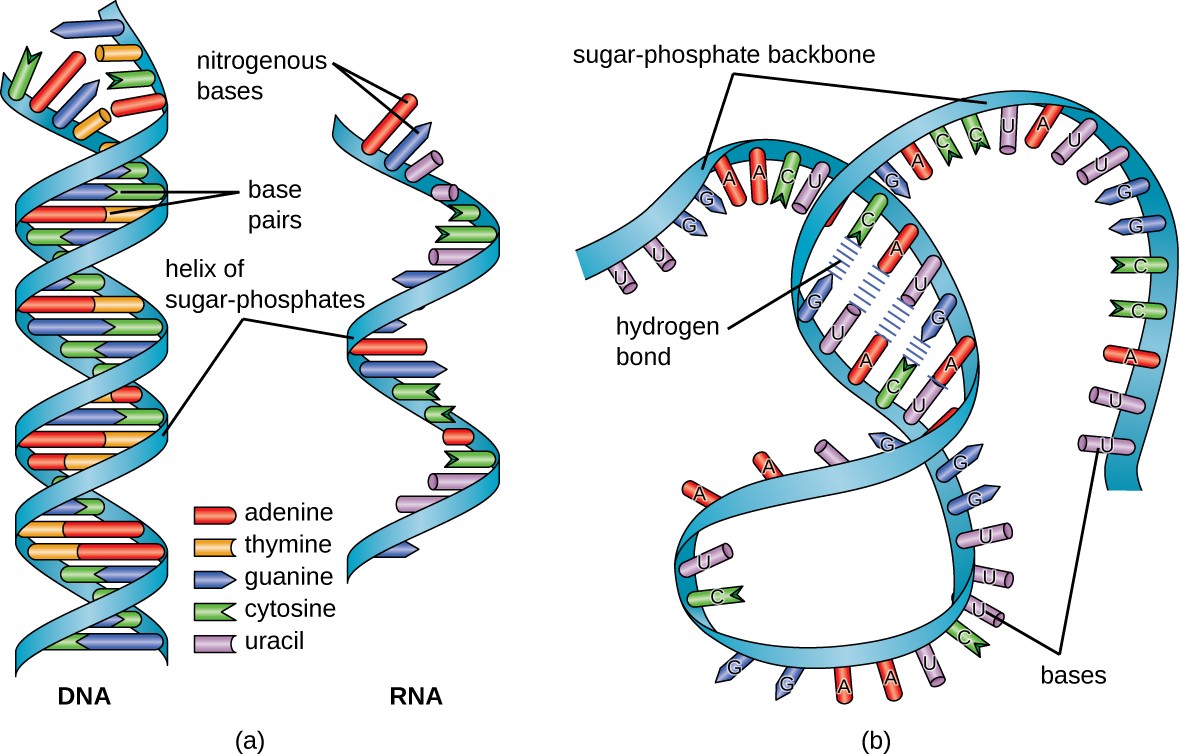
TRNA or Transfer RNA. A nucleotide contains a sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Transfer RNA tRNA is a short nucleotide RNA chain.
One molecule of ribonucleotide consists of. In the structure of tRNA the anticodon and the terminal 3 hydroxyl group are significant that takes part in ester linkage formation with amino acid and other features of its structure are the D and T-arm that support its high efficiency and specificity level. Transfer RNA is an RNA type that acts as the intermediary element and plays a significant role in the loading and transferring amino acids to the site of protein synthesis ie.
The two ribosomal RNA rRNA subunits join with proteins in the cytoplasm to form the subunits of ribosomes. -replicates itself when dividing. Structure of Transfer RNA Transfer RNA just like all molecules in the nucleic acid family is made of nucleotides.
Of the many types of RNA the three most well-known and most commonly studied are messenger RNA mRNA transfer RNA tRNA and ribosomal RNA rRNA which are present in all organisms. Transfer RNA is the third main type of RNA and one of the smallest usually only 7090 nucleotides long. RNA is single-stranded but in most RNA by means of intra-strand base pairing they.
Group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon. T-RNAtransfer RNA reads the genetic code on one hand transfers amino acids on the other hand so it is called an adapter molecule by Francis Crick. RNA is a type of nucleic acid found inside living cells.
Terms in this set 8 Transfer RNA tRNA type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. -provides code or template for the particular sequencing of amino acids that bond together and make a protein. What is Transfer RNA.
Flexibility in the base-pairing rules in which the. With a L-shaped structure tRNA functions as an adaptor molecule that translates three-nucleotide codon sequence in the mRNA into the suitable amino acid of that codon. It is a polymer of ribonucleotides.
Nitrogenous bases present in RNA are Adenine Guanine Cytosine and Uracil. Carries a specific amino acid and binds to the corresponding codon in messenger RNA during translation. Length DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA.
Ribosomal RNA rRNA is part of the ribosome or protein builders of the cell. Tranfer RNA tRNA indispensable RNA If this type of RNA is missing protein synthesis does not occur. Replicates and stores genetic information like a blueprint.
TRNA is a adaptor molecule with an L-shaped structure that translates three-nucleotide codon sequences in mRNA into the appropriate amino acid for that codon. Messenger RNA copies information from the DNA strand and takes that message to be decoded. They are ribonucleotides therefore they form a hydrogen bond with mRNA and form ester links with amino acids which.
The transfer RNAs are short molecules between the length of 70-90 nucleotides coded by several genes. Structure and Functions This is the non-coding RNA molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosomes from the growing peptide chain mRNA. Ribosomes help to build.
The amino acids then can be joined together and processed to make polypeptides and proteins. As there are 20 different amino acids there are also 20 different types of tRNA. An enzyme that joins each amino acid to the correct tRNA.
Transfer RNA tRNA is 15 of total RNA in cells. Transfer RNA tRNA is a carrier molecule for amino acids delivering them to the site of protein synthesis. The main function of RNA is to carry information of amino acid sequence from the genes to where proteins are assembled on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Types and functions of RNA. Like rRNA tRNA is located in the cellular cytoplasm and is involved in protein synthesis. T-RNA has five arms or loops.
The RNA portion of at least one cellular RNP has been shown to act as a biological catalyst a function previously ascribed only to proteins. The function of tRNA is to decode an mRNA sequence into a protein and transfer that protein to the ribosomes where DNA is replicated. Structure of t-RNA.
Transfer RNA brings or transfers amino acids to the ribosome that corresponds to each three-nucleotide codon of rRNA. Then the tRNA molecule attaches the amino acid to the amino acid chain and returns to the cytoplasm to do it all over again. As the link between amino acids and nucleic acids tRNAs determine the genetic code.
It carries the correct amino acid to the site of protein synthesis in the ribosome. Regarding this what is the function. Ribosomes are responsible for translation or the process our cells use to make proteins.
The nucleotide RNA chain transfer RNA tRNA is a short nucleotide RNA chain. Has an anticodon at one end and an amino acid attachment site at the other. The t-RNA first decodes the information or the nucleotide sequences carried by the m-RNA.
Transfer RNA tRNA is the third and the smallest type of RNA found in the cell. Its structure is bit complex as compared to messenger RNA mRNA it has 75-95 nucleotides in it. They do this through a highly complex sequence.
Transfer RNA tRNA is a small type of stable RNA that carries an amino acid to the corresponding site of protein synthesis in the ribosome. Therefore t-RNA also plays a major role in translating mRNA into proteins. There are 3 main types of RNA.
The tRNA decides what amino acid is needed according to the codon from the mRNA molecule. Ribosomal RNA decodes the message in the ribosome to make protein. It is also called as soluble RNA SRNA.
-stores an organisms genetic material in the nuclei. It is the base pairing between the tRNA and mRNA that allows for the correct amino acid to be inserted in the polypeptide chain being synthesized. Transfer RNA tRNA.
Molecular Biology Translation Transfer Rna Sparknotes

Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology

0 Response to "Describe the Structure and Function of Transfer Rna"
Post a Comment